For patients
Patient wellbeing is at the heart of the AIRS mission
Deciding to have surgery can be overwhelming, and it’s completely normal to have questions or concerns. In some cases, surgery may be the most suitable option for your condition. Your healthcare team will guide you through the information you need to make an informed choice about your treatment, including whether robotic surgery may be right for you.
Robotic surgery can offer significant benefits for patients and may be appropriate for a variety of procedures. Your medical team will consider your individual health needs and treatment goals to determine whether robotic surgery is the right choice for you.
Why choose robotic surgery?
Shorter recovery times
Research shows that patients who have robot-assisted surgery often recover faster and can leave hospital sooner. They may also have fewer post-operative complications and are usually able to get back to their normal routines earlier.
Smaller incisions and scars
Robotic surgery allows surgeons to operate with great precision, often using smaller incisions. This can mean faster recovery, smaller scars, and a reduced risk of infection. Research also shows that minimally invasive surgery, including robotic surgery, may cause less disruption to nearby organs and tissues, making it a helpful option when traditional surgery could lead to more side effects.
Higher surgical precision
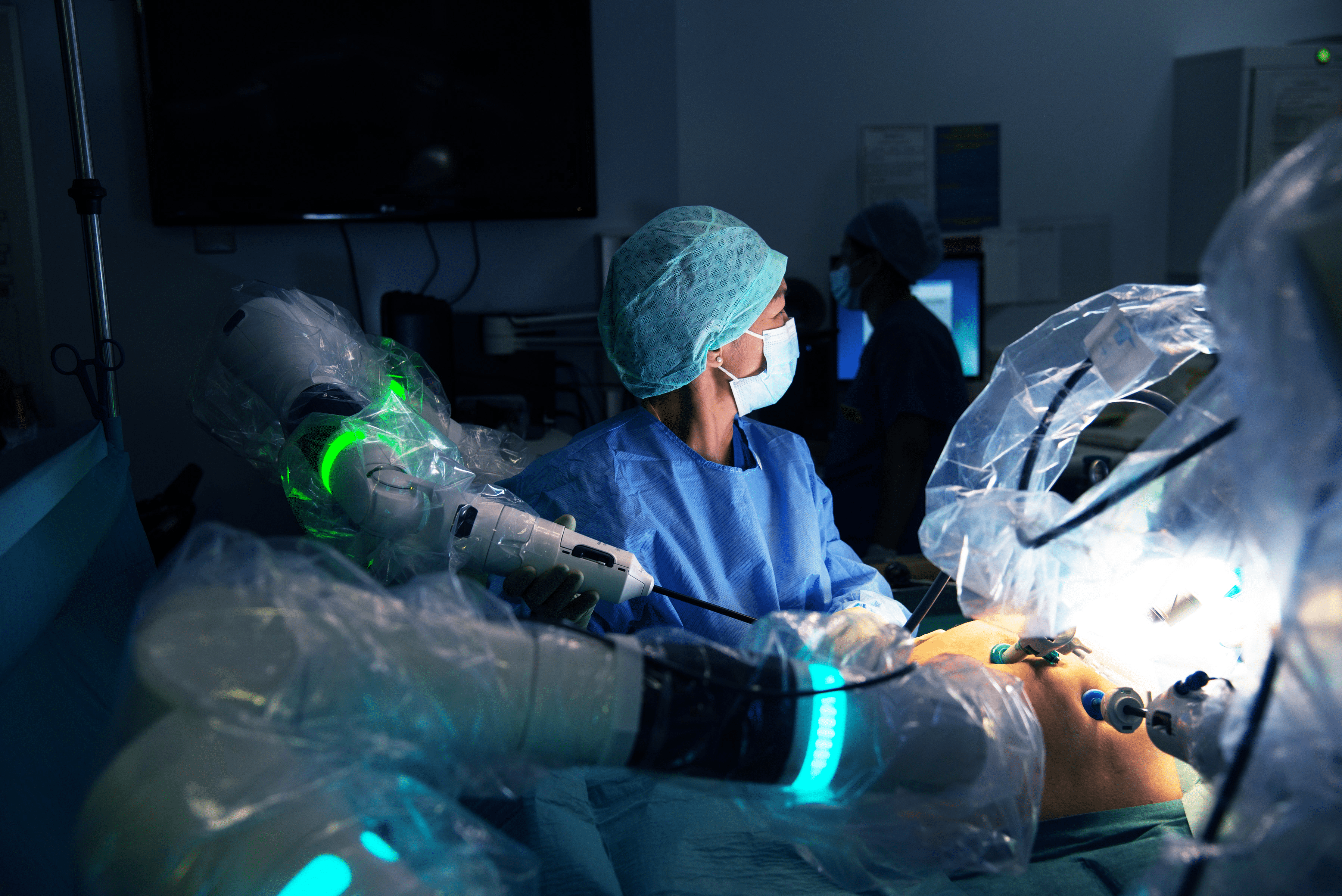
Surgical robots enable motion scaling, a process where large hand movements are translated into ultra-precise micromovements. This allows surgeons to perform procedures with a level of precision that would not be achievable with the human hand alone.
Surgeons also benefit from enhanced 3D, high-definition visualisation, providing a clearer and more detailed view of the surgical site than traditional methods.
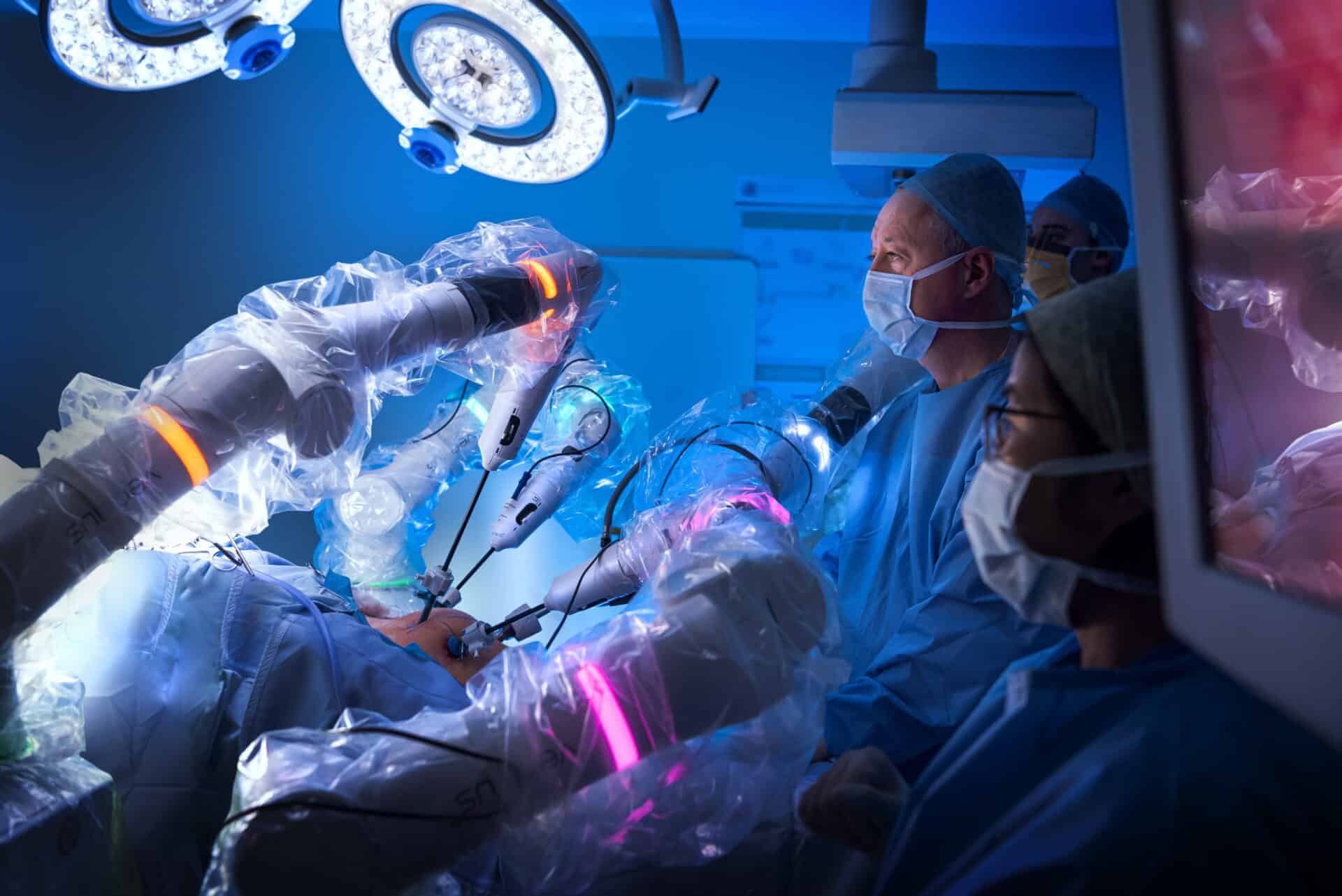
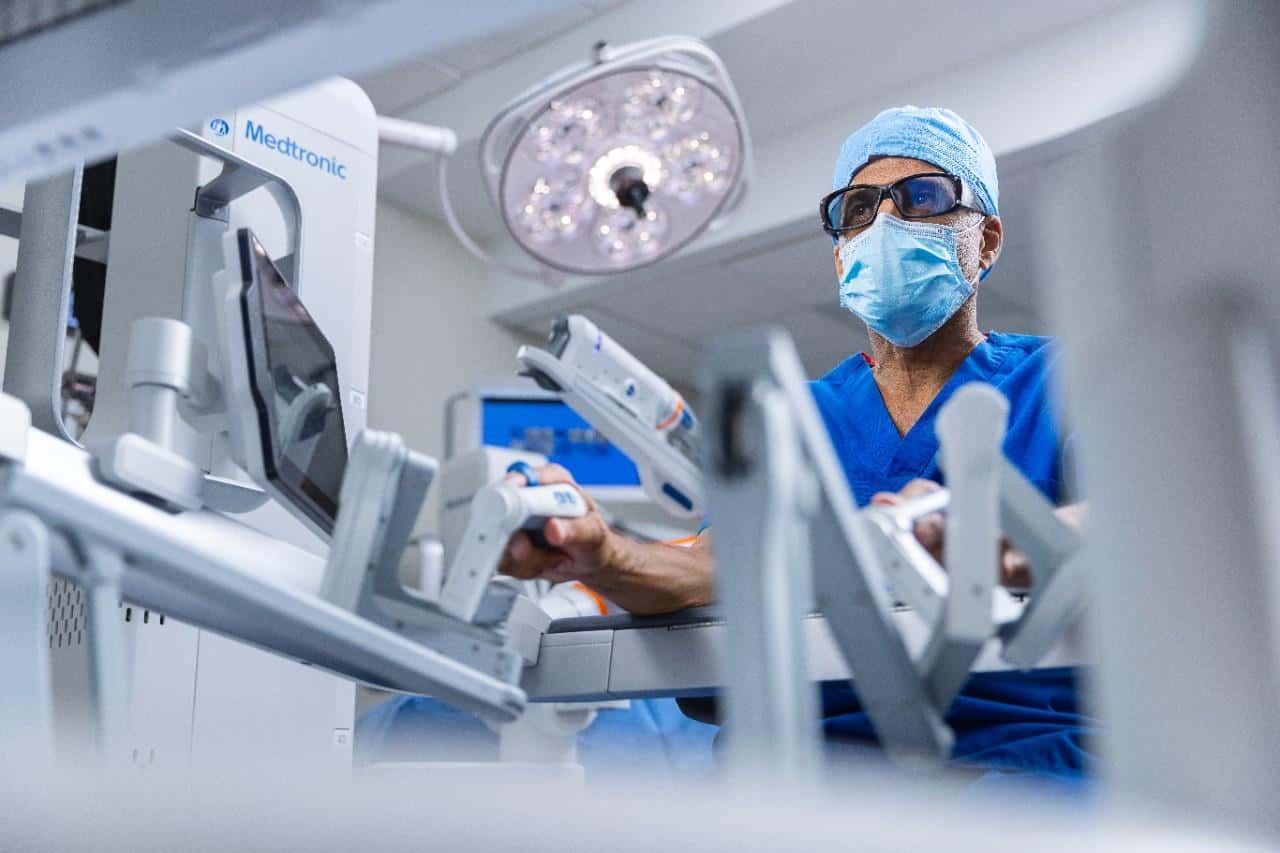
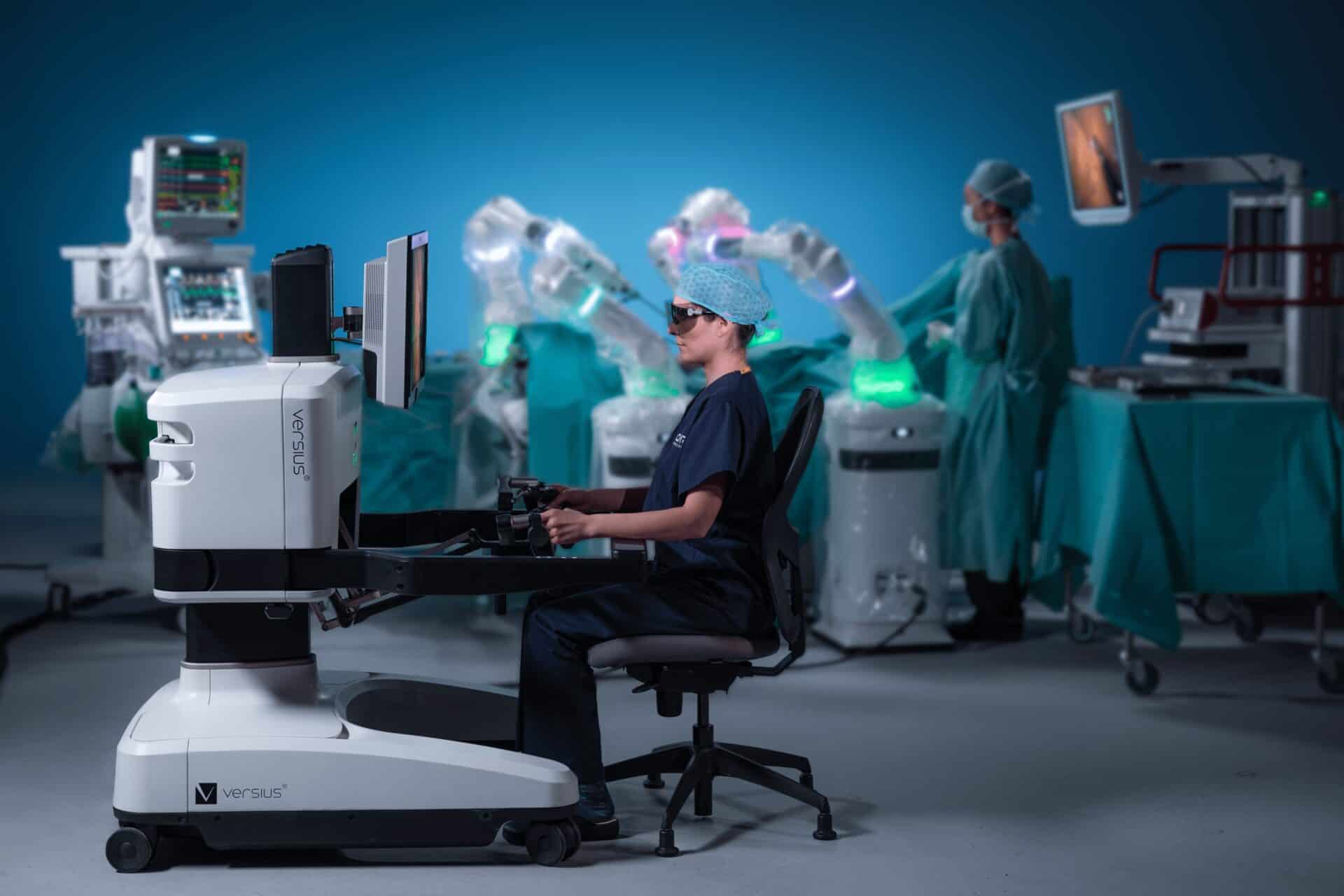
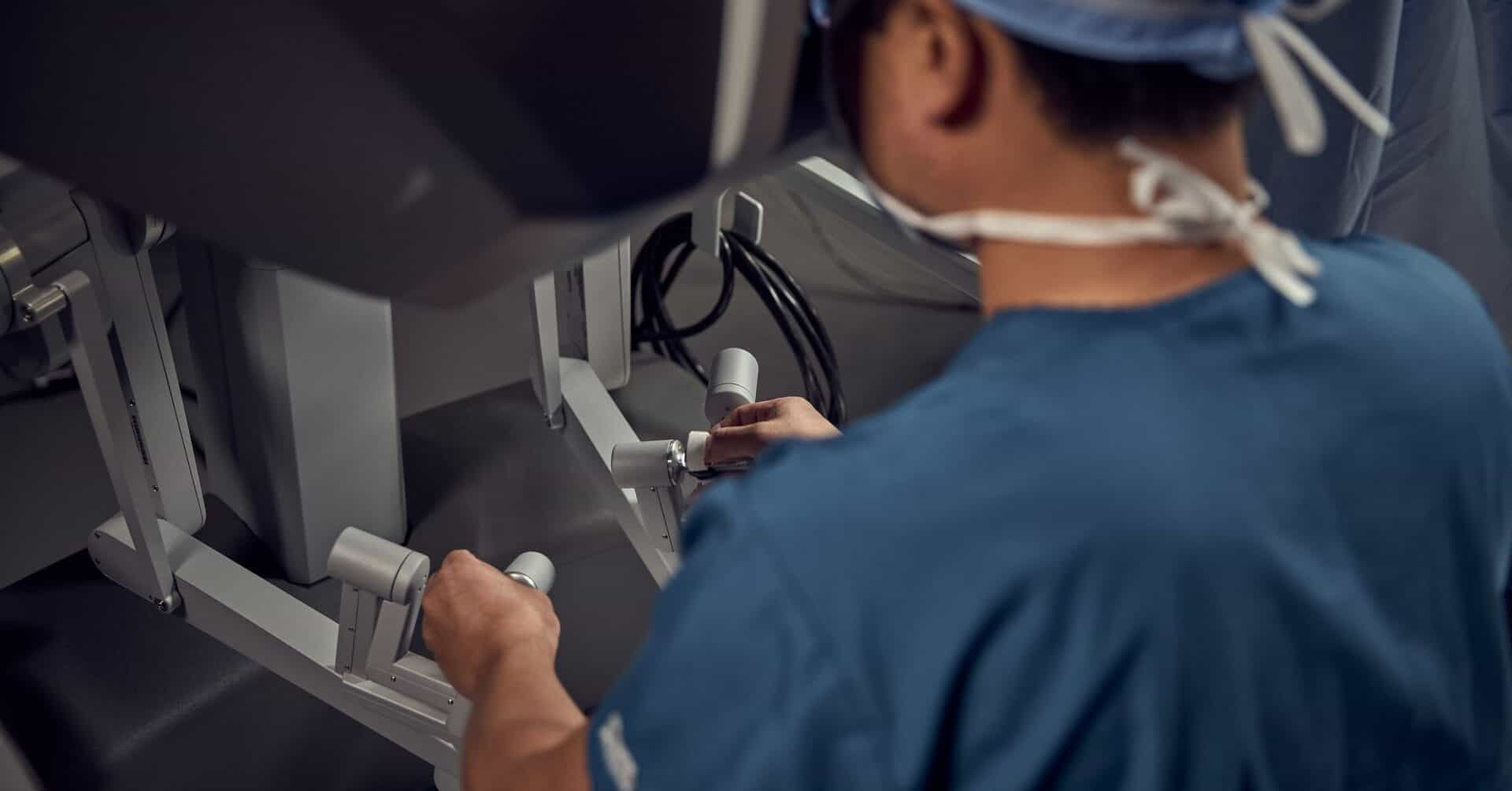
How it works
A qualified surgeon operates the robotic system from a console inside the operating theatre. Using their hands, fingers, and sometimes feet, the surgeon precisely controls the robot’s arms throughout the procedure. Your surgeon will be in the operating theatre with you at all times and remains in full control of every movement the robot makes. The robot does not act independently or make decisions on its own.
Our surgeons
With an AIRS accredited surgeon, your health is in good hands.
FAQs
Frequently asked questions
Robotic surgery is an exciting medical advancement, but it is completely normal to feel anxious about the idea of a robot being involved in your care. The name can be misleading. A qualified surgeon performs the entire operation, and the robot simply assists them as a tool. Your surgeon remains in full control at all times, and the robot cannot make decisions on its own.
What kind of surgery can be done robotically?
Robotic surgery is now used in many areas of medicine. You’ll see it most often in urology, gynaecology, and general surgery, but it is also used in orthopaedic, head and neck, heart, and chest operations.
Robotic surgery may not the right choice for everyone. Your healthcare team will talk through all of your options and help you decide on the approach that is best for you.
What does robotic surgery mean?
Robotic surgery refers to minimally invasive surgery performed using a robotic surgical system. The surgeon operates the robot throughout the procedure and remains fully responsible for every movement. Although the term suggests otherwise, the surgery is not performed by a robot.
How safe is robotic surgery?
All surgery involves some risk, but the features of robotic surgery, including smaller incisions, shorter hospital stays and improved surgical precision, can help make the experience safer and support a smoother recovery for many patients.
Who benefits from robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery has advantages for both patients and surgeons.
Patients may recover more quickly, spend less time in hospital, have fewer complications and often have smaller scars.
Surgeons benefit from a more comfortable working position, a highly magnified 3D view of the area they are operating on and easier access to small or difficult-to-reach areas.